[ad_1]
In the course of purely curious exploration, the JACO arm discovers how to select up cubes, moves them all-around the workspace and even explores whether they can be well balanced on their edges.
Curious exploration enables OP3 to walk upright, harmony on a person foot, sit down and even catch alone safely and securely when leaping backwards – all with no a precise target undertaking to optimise for.
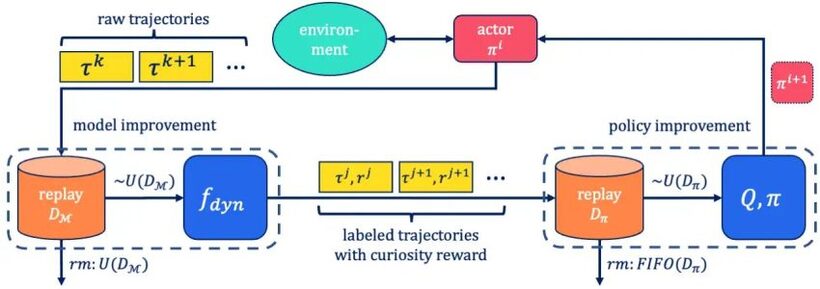
Intrinsic drive [1, 2] can be a powerful strategy to endow an agent with a mechanism to repeatedly discover its natural environment in the absence of activity facts. One frequent way to apply intrinsic motivation is by way of curiosity mastering [3, 4]. With this process, a predictive design about the environment’s reaction to an agent’s steps is experienced alongside the agent’s policy. This model can also be named a world product. When an motion is taken, the world design would make a prediction about the agent’s future observation. This prediction is then when compared to the correct observation designed by the agent. Crucially, the reward given to the agent for using this action is scaled by the mistake it manufactured when predicting the future observation. This way, the agent is rewarded for using actions whose outcomes are not but nicely predictable. At the same time, the world product is current to improved forecast the end result of reported motion.
This mechanism has been used effectively in on-policy options, e.g. to defeat 2D pc game titles in an unsupervised way [4] or to coach a general coverage which is simply adaptable to concrete downstream jobs [5]. On the other hand, we think that the true energy of curiosity studying lies in the numerous behaviour which emerges during the curious exploration method: As the curiosity aim variations, so does the ensuing conduct of the agent therefore discovering quite a few intricate guidelines which could be utilised later on, if they have been retained and not overwritten.
In this paper, we make two contributions to study curiosity finding out and harness its emergent behaviour: 1st, we introduce SelMo, an off-plan realisation of a self-motivated, curiosity-primarily based strategy for exploration. We present that using SelMo, significant and assorted conduct emerges solely based mostly on the optimisation of the curiosity objective in simulated manipulation and locomotion domains. 2nd, we suggest to lengthen the target in the software of curiosity finding out in the direction of the identification and retention of emerging intermediate behaviours. We assistance this conjecture with an experiment which reloads self-identified behaviours as pretrained, auxiliary abilities in a hierarchical reinforcement studying set up.

We run SelMo in two simulated continual handle robotic domains: On a 6-DoF JACO arm with a a few-fingered gripper and on a 20-DoF humanoid robot, the OP3. The respective platforms existing difficult finding out environments for item manipulation and locomotion, respectively. Even though only optimising for curiosity, we notice that complicated human-interpretable conduct emerges in excess of the training course of the teaching operates. For occasion, JACO learns to decide up and go cubes with out any supervision or the OP3 learns to equilibrium on a one foot or sit down properly devoid of falling in excess of.
.jpg)
.jpg)
Nevertheless, the impressive behaviours noticed through curious exploration have a single crucial downside: They are not persistent as they retain switching with the curiosity reward operate. As the agent retains repeating a selected conduct, e.g. JACO lifting the red dice, the curiosity rewards amassed by this coverage are diminishing. Therefore, this leads to the learning of a modified coverage which acquires bigger curiosity benefits yet again, e.g. going the cube outdoors the workspace or even attending to the other dice. But this new conduct overwrites the old one. Having said that, we feel that retaining the emergent behaviours from curious exploration equips the agent with a valuable skill established to master new responsibilities much more immediately. In purchase to investigate this conjecture, we set up an experiment to probe the utility of the self-discovered competencies.
.jpg)
We treat randomly sampled snapshots from unique phases of the curious exploration as auxiliary abilities in a modular finding out framework [7] and measure how speedily a new goal talent can be realized by utilizing individuals auxiliaries. In the situation of the JACO arm, we set the target undertaking to be “lift the crimson dice” and use five randomly sampled self-found behaviours as auxiliaries. We compare the finding out of this downstream job to an SAC-X baseline [8] which works by using a curriculum of reward functions to reward achieving and transferring the pink dice which in the end facilitates to understand lifting as effectively. We locate that even this uncomplicated setup for talent-reuse already speeds up the mastering development of the downstream task commensurate with a hand created reward curriculum. The outcomes counsel that the automated identification and retention of useful rising behaviour from curious exploration is a fruitful avenue of potential investigation in unsupervised reinforcement mastering.
[ad_2]
Source link